Interventional Procedure
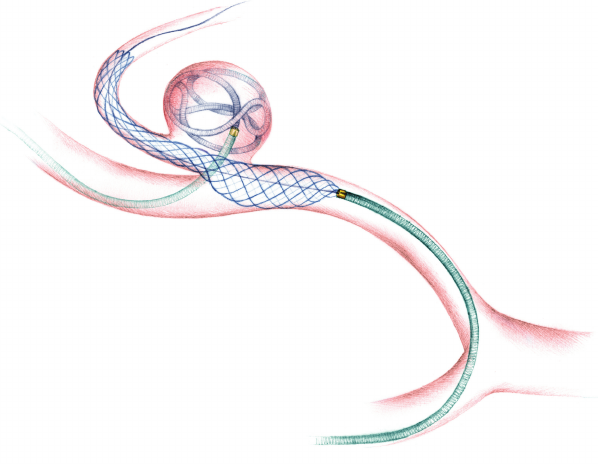
Brain Aneurysm Coiling
Procedure Date
February 2018
In the Media
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/goa/docs-perform-brain-aneurysm-coiling/articleshow/46292111.cms

Introduction
A brain aneurysm, also known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), is a weak spot in the wall of a blood vessel inside the brain.
That area of the blood vessel gets worn out from the constant flow of blood and bulges out, almost like a bubble. It can grow to the size of a small berry. It has the risk of rupturing and leading to bleeding in the brain cavity.
Diagnosis & Treatement
A 42-year-old Russian was complaining of severe headache, vomiting and loss of consciousness.
On further evaluation of the brain arteries with CT angiography, it was found that the right posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA), a small artery in the posterior portion of the brain, had a ruptured aneurysm arising from its wall.
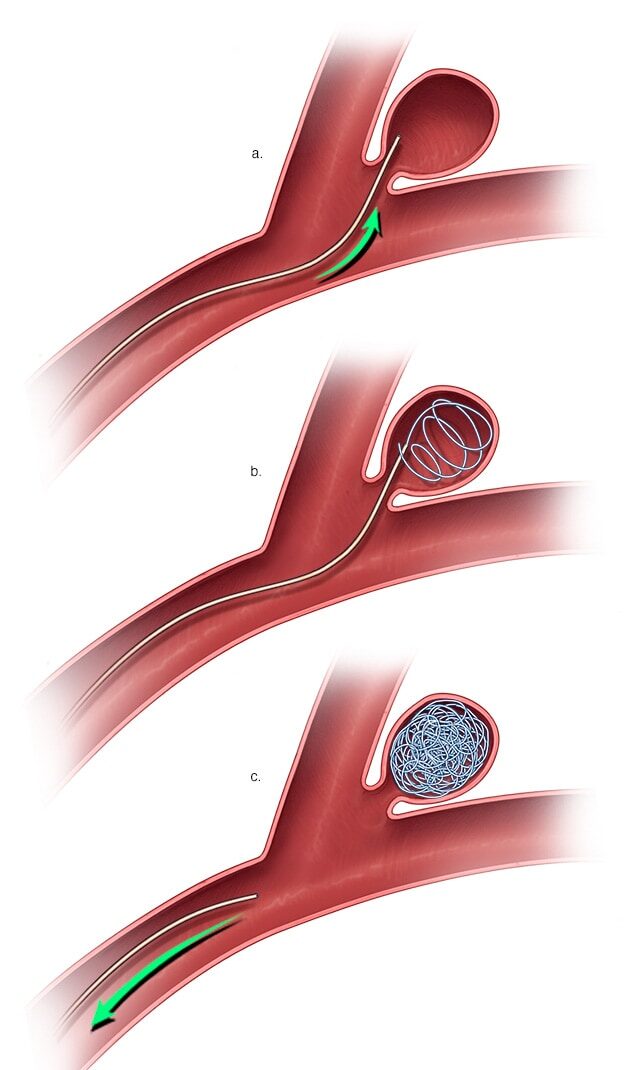
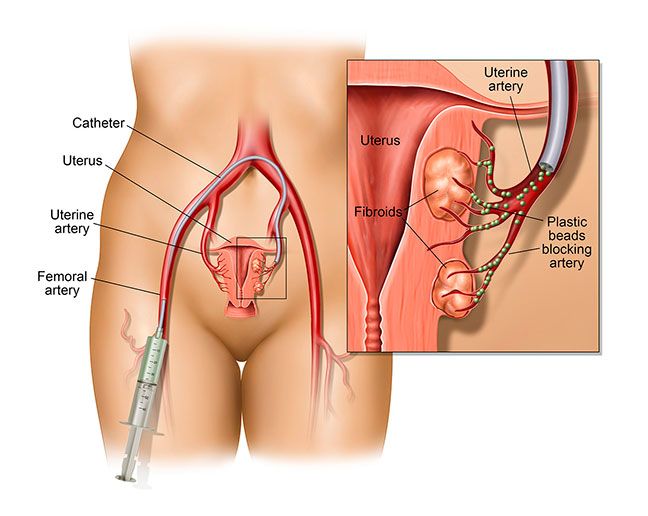
As an emergency, the patient was taken up for aneurysm coiling”. The aneurysm coiling, also called endovascular coiling, was performed by Dr. Charudutt Sambhaji and Dr. Keerthiraj, both vascular and interventional radiologists at Manipal hospital Goa in a procedure that lasted for around two-and-a-half hours.
When an aneurysm ruptures it results in a catastrophic brain hemorrhage. Ten to 15% of these patients die before reaching the hospital, with more than 50% of fatalities occurring in the first 30 days after rupture. Of those who survive, approximately half suffer some permanent neurological deficit. PICA aneurysms, the type identified in the patient is among the rare and technically difficult aneurysms to treat by coiling
Conclusion
In a first of its kind, rare procedure was performed to save the life of a patient suffering from a brain aneurysm and internal hemorrhage. The patient recovered successfully without any complications.